Mono-PERC Half-Cut
Industry StandardTypical Cost: Economic
Proven reliability and the best ROI for standard residential roofs.
Bifacial Mono
Double-Sided YieldTypical Cost: Mid-Range
Captures reflected light from the ground. Ideal for carports or tilt-mounts.

TOPCon (N-Type)
High EfficiencyTypical Cost: Premium
N-type wafers offer lower degradation and better performance on cloudy days.
HJT Tech
Advanced HybridTypical Cost: High-End
Combines Crystalline and Thin-film. Best for extremely hot climates.
Old Technologies
Monocrystalline (Mono)
Panels made from a single, pure crystal of silicon. Recognizable by their uniform dark/black color and rounded edges.
Efficiency: Highest efficiency (17-22%+).
Space: Requires less roof space for the same power output.
Aesthetics: Considered the most attractive (all-black look).
Cost: Highest cost per panel.
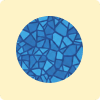
Polycrystalline (Poly)
Panels made from multiple melted silicon fragments. Recognizable by their square cells and blue, mottled appearance.
Efficiency: Good, standard efficiency (15-17%).
Space: Requires more roof space than mono panels for the same power.
Cost: Lowest manufacturing cost, offering better budget value.
Best For: Large roofs where space is not a limiting factor.
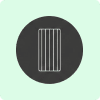
Thin-Film (Amorphous)
Panels made by depositing a thin layer of photovoltaic material (like cadmium telluride) onto a substrate.
Efficiency: Lowest efficiency (7-13%).
Flexibility: Can be flexible or rolled out, making them highly versatile.
Performance: Excellent low-light performance and less heat sensitivity.
Best For: Non-traditional applications, commercial installations, or curved surfaces.
Panel Comparison Summary
| Feature | Monocrystalline | Polycrystalline | Thin-Film |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material Purity | Single, pure silicon crystal | Multiple silicon fragments | Non-silicon compounds (CdTe, etc.) |
| Typical Appearance | Uniform Black/Dark Blue | Mottled/Slightly Blue | Uniform, often dark gray/light black |
| Efficiency Range | 17% – 22%+ (Highest) | 15% – 17% (Standard) | 7% – 13% (Lowest) |
| Space Efficiency | Best (Needs less roof space) | Good (Needs more roof space) | Poor (Needs most roof space) |
| Cost per Watt | Highest | Lowest | Varies (Low materials cost, higher installation complexity) |
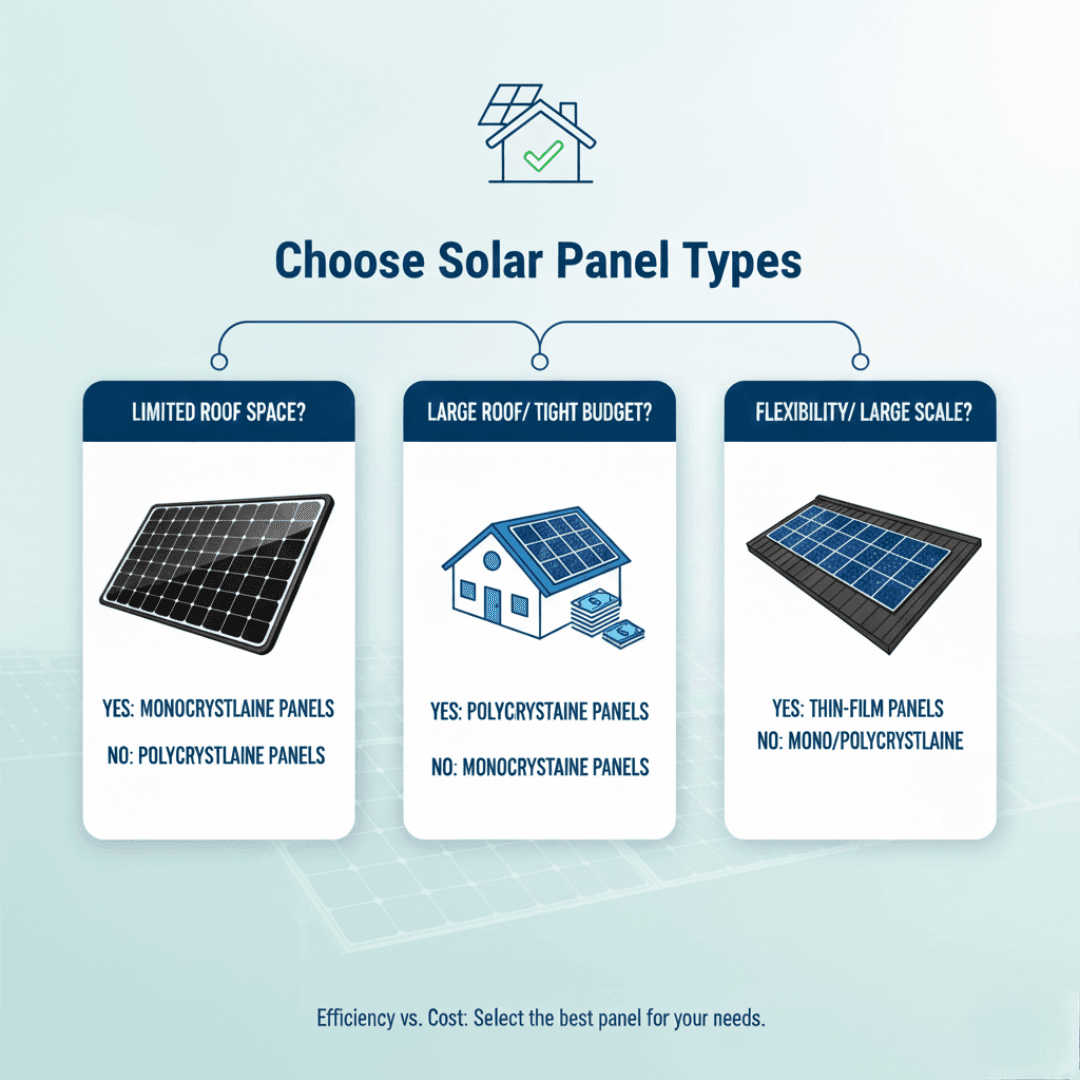
Which Panel Type is Right for Your Home?
The choice between panel types is often a trade-off between maximizing power (efficiency) and minimizing cost (budget).
If your roof space is limited or you prioritize aesthetics: Choose Monocrystalline panels. Their higher efficiency means you get more power from fewer panels, and their uniform black look is visually appealing.
If you have a large, open roof and a tight budget: Choose Polycrystalline panels. They offer excellent value and are a proven, reliable technology, assuming space is not a constraint.
If you have a large commercial building or non-traditional surfaces: Consider Thin-Film panels. Their lightweight nature and flexibility make them ideal for specialized, large-scale applications.


