Panel Comparison Summary
| Factor | Galvanized Iron (GI) | Aluminum (Al) | Stainless Steel (SS) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | Good (Zinc coating protects it, but coating can degrade) | Excellent (Naturally non-corrosive) | Superior (Highest resistance to rust/chemicals) |
| Strength & Load Bearing | Highest (Excellent for heavy loads and high winds) | High (Adequate for standard residential loads) | Extremely High (Often used for critical small parts) |
| Weight | Heavy (Adds significant dead load to the roof) | Very Light (Minimal roof load) | Heavy |
| Cost (Relative) | Lowest | High (Premium option) | Highest |
| Life Expectancy | 20 - 25 years (Dependent on zinc quality/environment) | 25+ years | 50+ years |

Corrosion Details & Maintenance
Corrosion is the single biggest threat to the structural integrity of your solar system. Proper material choice is vital for long-term safety and performance.
- Galvanic Corrosion Risk: When Aluminum and GI/Steel are placed in direct contact (especially when wet), a chemical reaction can occur, rapidly corroding the less noble metal (Aluminum). This is why non-metallic separators or specialized fasteners must be used in mixed-metal systems.
- GI Maintenance: The life of GI depends entirely on the thickness and quality of its zinc coating. In coastal areas or industrial zones, the zinc wears off faster. It may require periodic inspection for rust, unlike aluminum.
- Aluminum's Advantage: Aluminum forms a natural, thin layer of aluminum oxide when exposed to air. This layer is highly resistant to further oxidation, giving it its superior corrosion resistance without heavy coatings.
Structural & Location Considerations
The ideal material also depends on the local climate and the type of structure being installed on.
- Wind and Seismic Zones: In areas prone to high wind loads (cyclone/hurricane zones) or seismic activity, the inherent strength of GI (Steel) is often necessary to meet stringent building codes, despite its weight.
- Roof Type Compatibility: Lightweight Aluminum structures are preferred for older residential rooftops that may not have been structurally designed to handle the heavy load of GI frameworks.
- Ground Mounts: For large-scale ground-mounted projects, GI is often used for the main framework and support poles because the heavy weight is beneficial for stability, and cost efficiency is paramount.

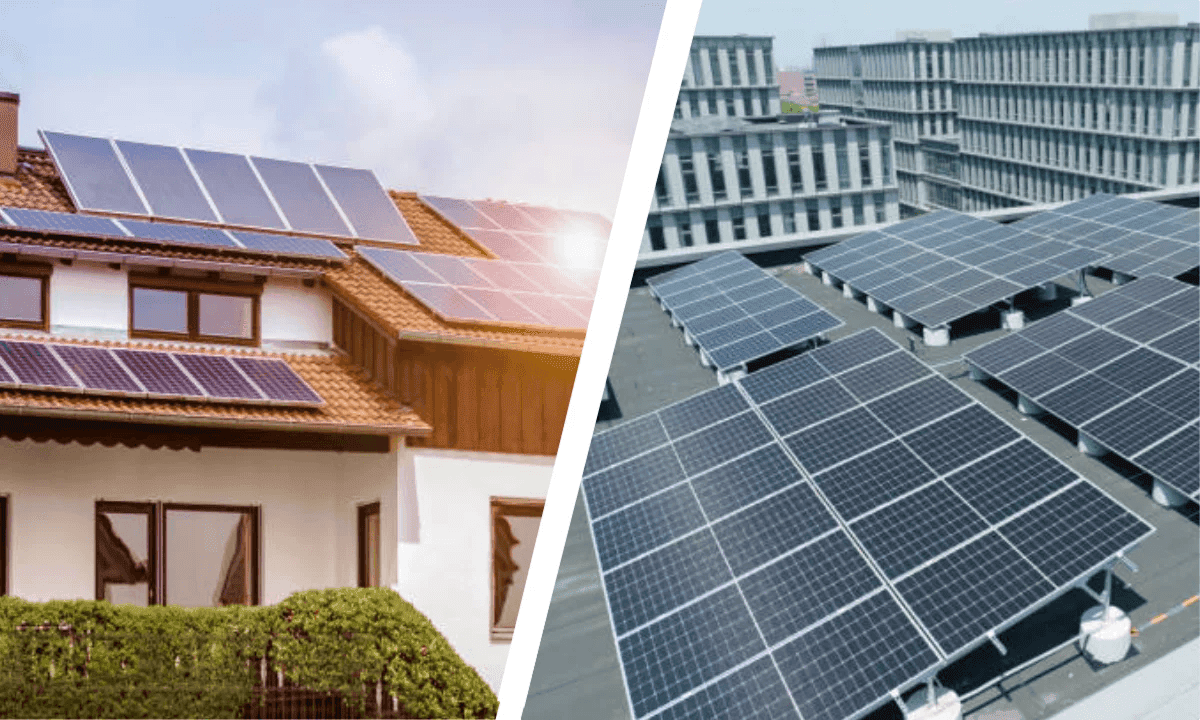
Choosing the Right Material for Your Installation
- Budget-Focused Projects: GI is the optimal choice. It provides the necessary strength and durability at the lowest cost, making solar more accessible.
- Roof Weight Constraints: If your roof structure is older or has strict weight limitations, Aluminum is highly recommended to minimize the load.
- Corrosive Environments: For coastal areas, near chemical plants, or regions with high humidity/salt content, the natural resistance of Aluminum is often preferred over GI.
- Large Ground Mounts or Heavy Systems: The immense structural integrity of GI often makes it the default choice for large-scale, heavy-duty ground-mounted projects where weight is not an issue.
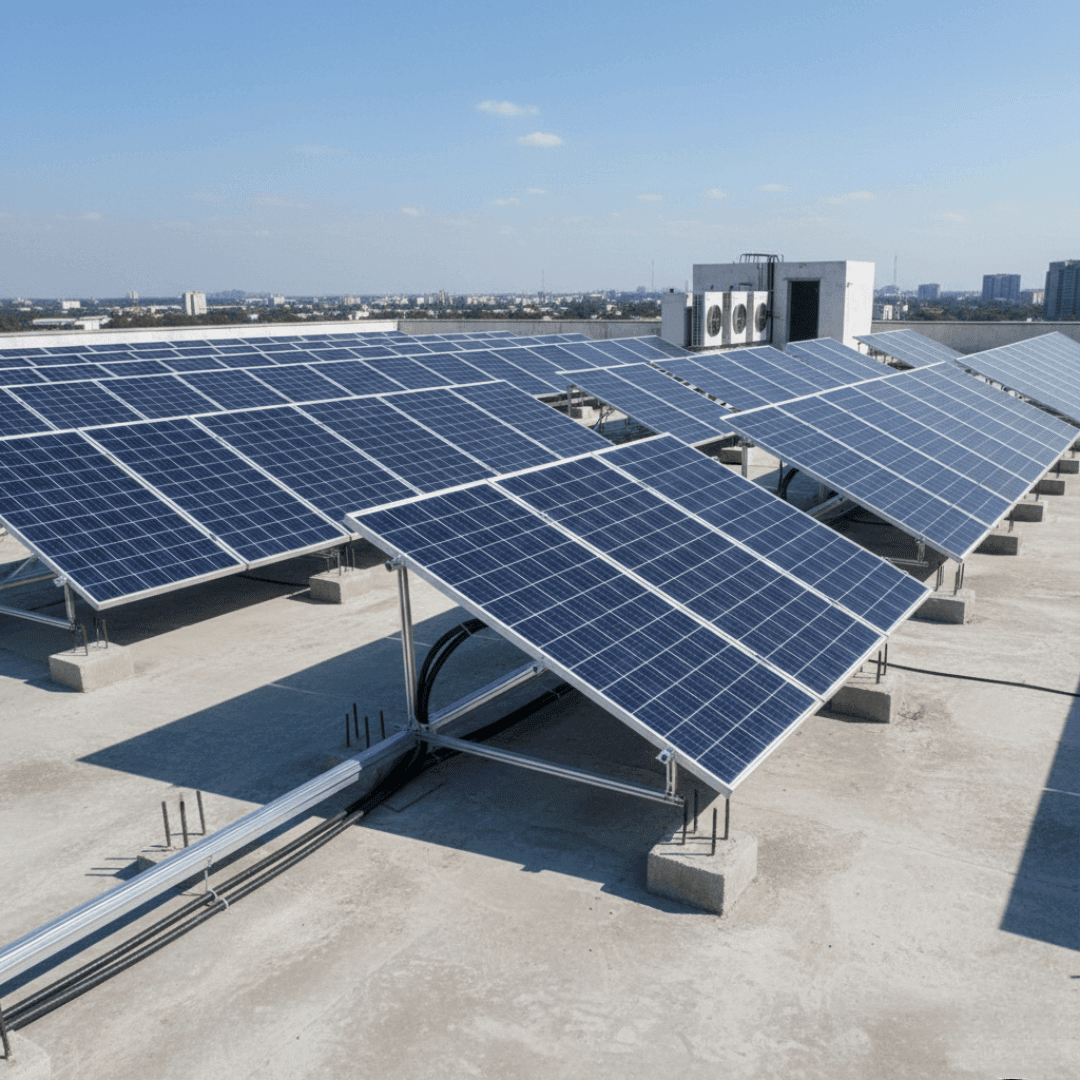
RCC Roof Mounting Structure
RCC mounting structures are used to install solar panels on concrete rooftops, making them the standard choice for residential and commercial buildings. By keeping the panels close to the inverter, these systems reduce wiring needs and minimize DC power losses.
While cost-effective, these structures require roof penetration. It is critical to seal drill points properly to prevent leaks. Additionally, performance depends heavily on the roof’s orientation and ensuring the area is shadow-free.
Pros:
• Easy to maintain
• Uses the unutilized roof space for energy generation
• Protects the roof underneath
Cons:
• The roof should be shadow free and provide space for the correct orientation
• Difficult to scale up the system
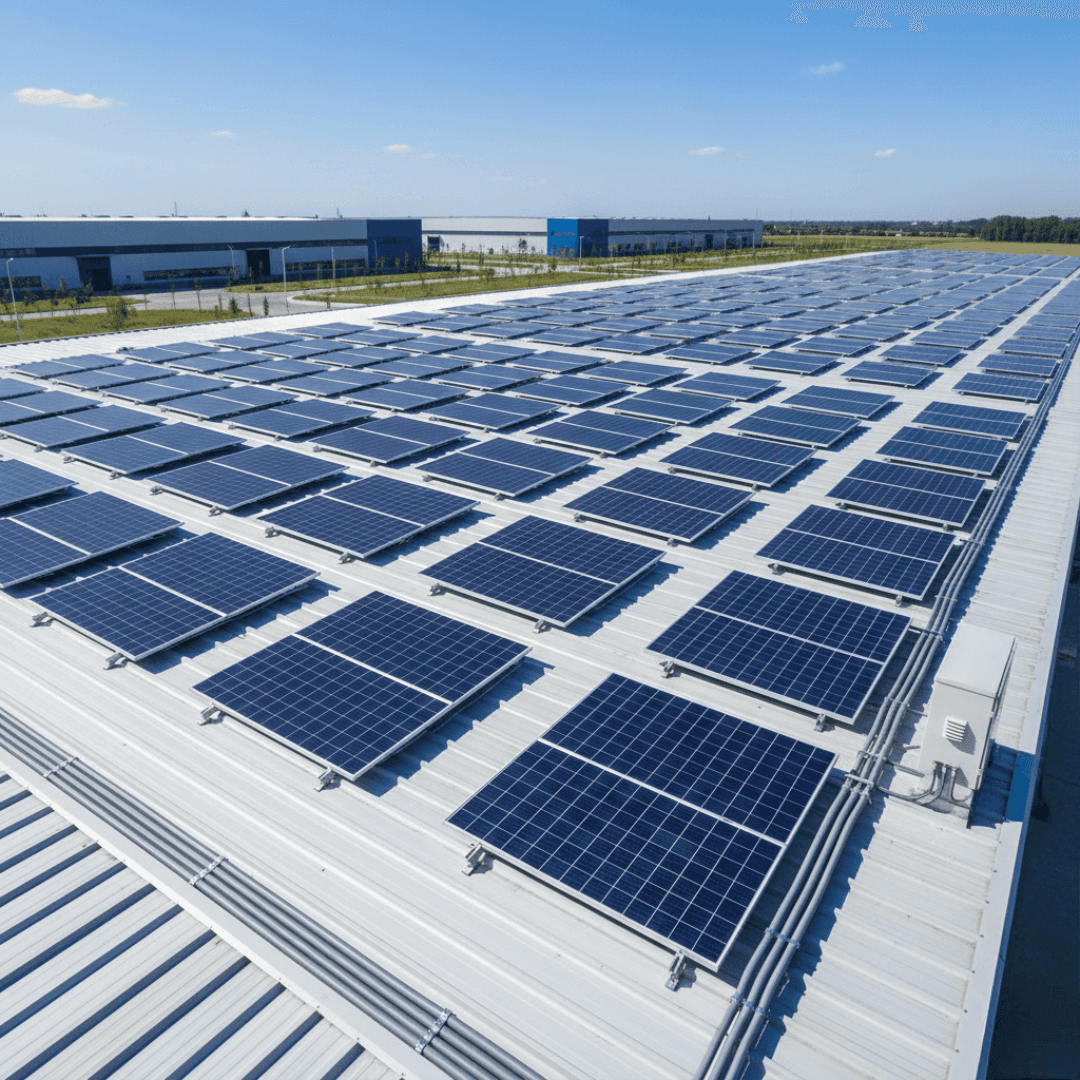
Shed Mounting Structures
Shed mounts are rooftop structures specifically designed for metal or corrugated sheet roofing. While used occasionally in residential settings, they are the primary choice for commercial and industrial (C&I) sectors.
Business owners typically install these on factories, warehouses, and industrial sheds to lower operational costs and achieve energy independence.
Pros:
• Easy to maintain
• Turns the unused roof space into an energy generation spot
Cons:
• Requires shadow-free roof space to set up panels
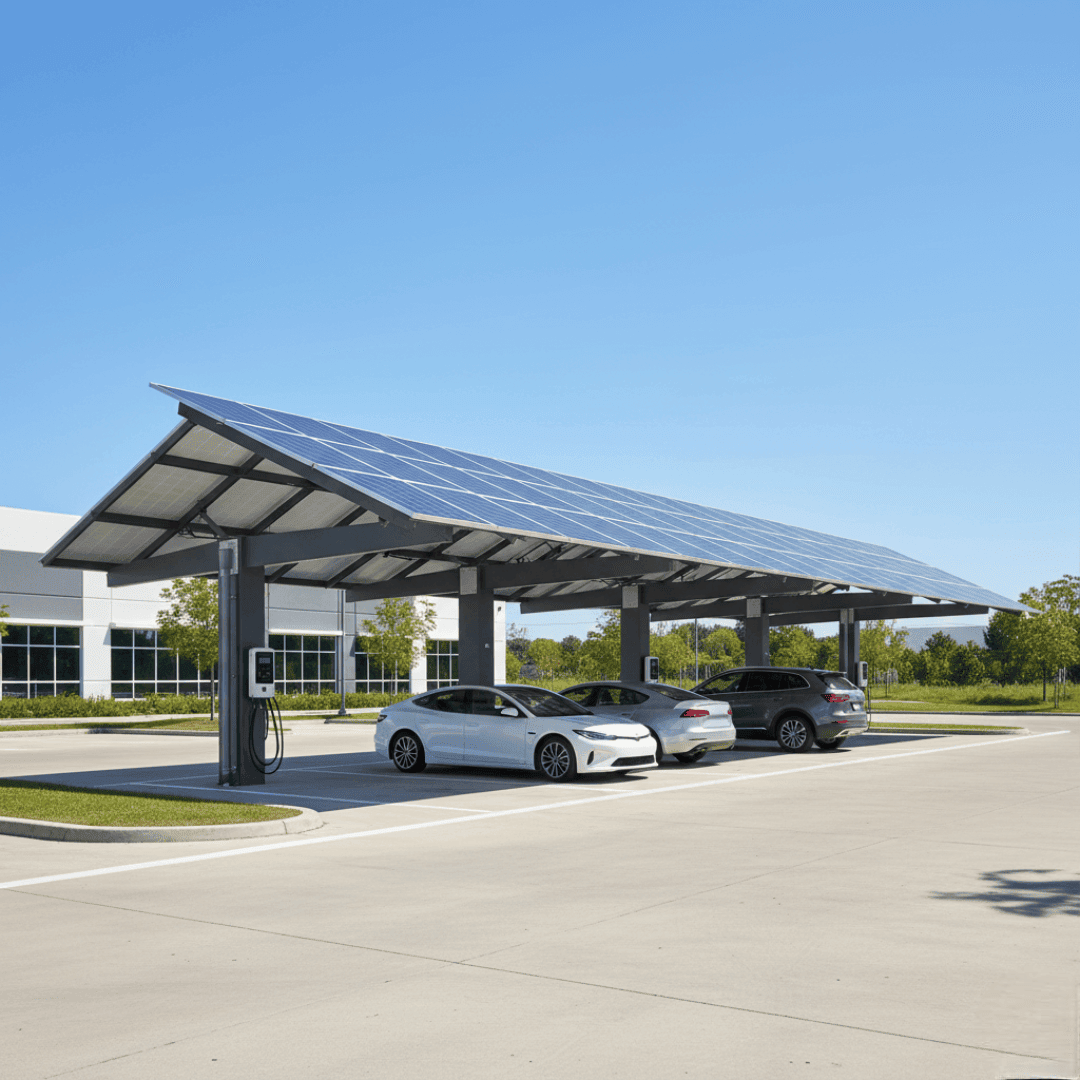
Carport Mounting Structure
Carports are elevated ground-mounted structures designed to provide enough clearance for vehicles to park underneath. They turn parking lots and driveways into efficient energy-generating zones.
These structures are popular for both residential and commercial use, as they can be easily integrated with EV charging stations and add a modern, sleek aesthetic to the property.
Pros:
• Utilizes underused spaces for energy generation
• Provides dual function of energy generation and providing shade
Cons:



